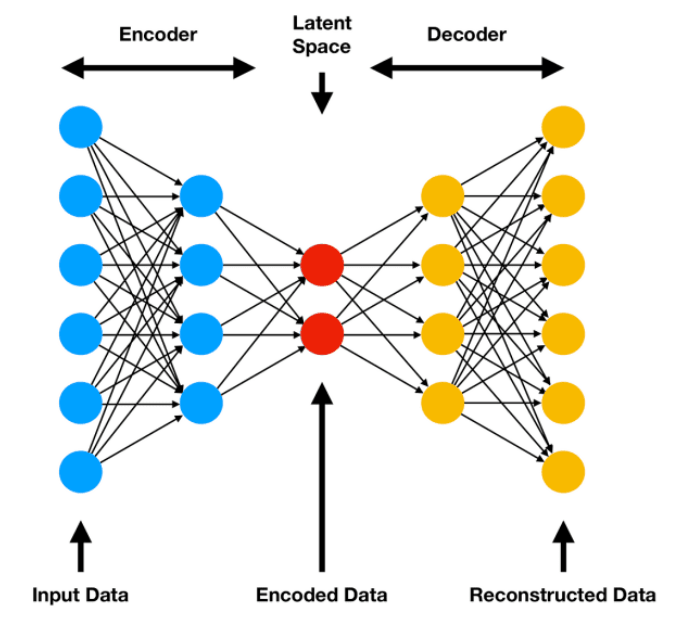
How Autoencoders Work
- Input Layer: Accepts input data (e.g., images, numerical data, etc.) for compression and reconstruction.
- Encoder: - Compresses the input data into a smaller latent representation. - Captures essential features by reducing dimensionality through successive layers.
- Latent Space: The encoded representation of the input data that holds the most critical information.
- Decoder: - Expands the latent representation back into the original data dimensions. - Attempts to reconstruct the input as accurately as possible.
- Output Layer: Produces the reconstructed data, comparing it to the input data for accuracy.
- Applications: - Data denoising - Dimensionality reduction - Feature extraction - Image generation (e.g., with Variational Autoencoders)
Autoencoder Architecture Code Example
Here's how we can define the layers of an Autoencoder:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
def build_autoencoder(input_shape):
"""
Autoencoder Model
:param input_shape: Shape of the input data (e.g., (28, 28, 1) for grayscale images)
"""
# Encoder
encoder_input = layers.Input(shape=input_shape, name="encoder_input")
x = layers.Conv2D(32, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same", activation="relu")(encoder_input)
x = layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same", activation="relu")(x)
encoded = layers.Flatten()(x)
encoded = layers.Dense(128, activation="relu", name="encoded")(encoded)
# Decoder
x = layers.Dense(7 * 7 * 64, activation="relu")(encoded) # Upsample to match encoder dimensions
x = layers.Reshape((7, 7, 64))(x)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same", activation="relu")(x)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(32, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same", activation="relu")(x)
decoded = layers.Conv2DTranspose(1, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding="same", activation="sigmoid", name="decoded")(x)
# Autoencoder Model
autoencoder = tf.keras.Model(encoder_input, decoded, name="autoencoder")
return autoencoder
# Instantiate the Autoencoder Model
input_shape = (28, 28, 1) # Example: grayscale image input
autoencoder_model = build_autoencoder(input_shape)