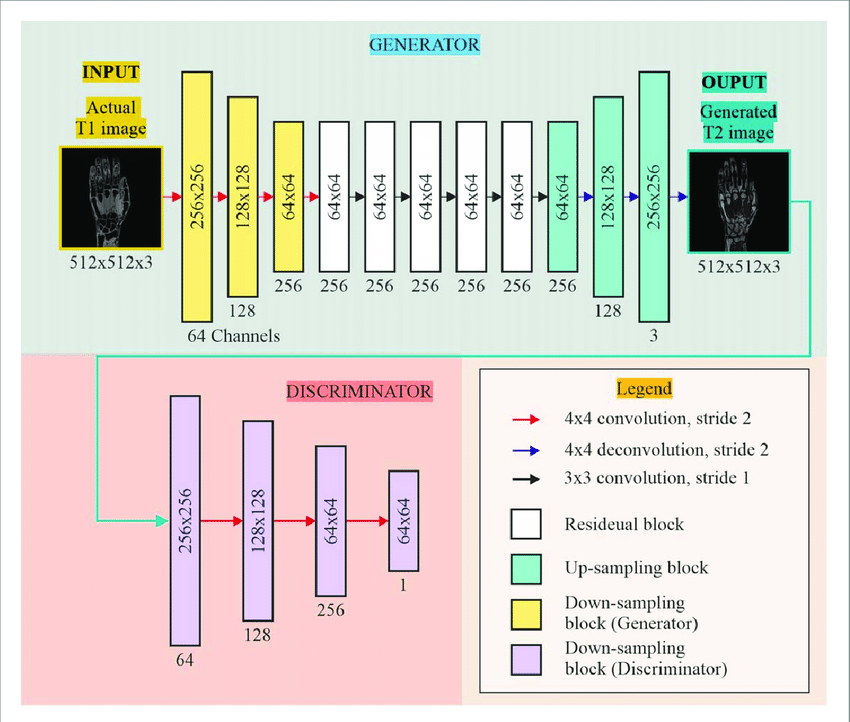
How Cycle GANs Work
- Input: Takes an input image (e.g., T1 image) to be translated into another domain (e.g., T2 image).
- Generator: - Converts the input image into the target domain using: - **Downsampling blocks** (4x4 convolution with stride 2). - **Residual blocks** (3x3 convolution with stride 1) to retain features. - **Upsampling blocks** (4x4 deconvolution with stride 2) to restore original dimensions. - Produces a generated image in the target domain.
- Discriminator: - Evaluates the authenticity of the generated image. - Uses downsampling blocks to classify images as real or fake.
- Cycle Consistency: - Ensures that translating an image to the target domain and back to the original domain reproduces the original image.
- Adversarial Loss: Guides the generator to produce realistic images that can fool the discriminator.
- Applications: - Image-to-image translation (e.g., T1 to T2 MRI scans). - Style transfer (e.g., transforming photographs into paintings). - Cross-domain data augmentation.
CycleGAN Code Example
Here's how we can define a simplified CycleGAN:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
# Generator Model
def build_generator():
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Input(shape=(128, 128, 3)), # Input Layer (e.g., 128x128 RGB image)
layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=7, strides=1, padding="same", activation="relu"), # Conv Layer
layers.Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same", activation="relu"), # Down-sample
layers.Conv2D(256, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same", activation="relu"), # Down-sample
layers.Conv2DTranspose(128, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same", activation="relu"), # Up-sample
layers.Conv2DTranspose(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same", activation="relu"), # Up-sample
layers.Conv2D(3, kernel_size=7, strides=1, padding="same", activation="tanh") # Output Layer
])
return model
# Discriminator Model
def build_discriminator():
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Input(shape=(128, 128, 3)), # Input Layer (128x128 RGB image)
layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=4, strides=2, padding="same", activation="relu"), # Conv Layer
layers.Conv2D(128, kernel_size=4, strides=2, padding="same", activation