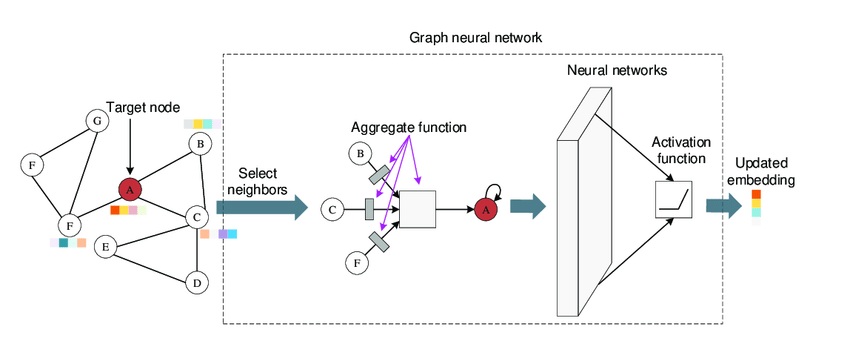
How GNNs Work
- Input: A graph structure with nodes and edges, where nodes represent entities, and edges represent relationships.
- Neighbor Selection: - For each target node, its neighbors are identified based on graph connectivity. - Neighboring nodes provide local context for the target node.
- Aggregation Function: - Combines the features of the selected neighbors. - Common aggregation methods include mean, sum, or max pooling.
- Neural Network Transformation: - Aggregated features are passed through a neural network. - An activation function (e.g., ReLU, Sigmoid) introduces non-linearity to the transformations.
- Updated Embedding: The target node’s representation is updated, reflecting its features and its neighborhood structure.
- Applications: - Social networks (e.g., friend recommendations). - Knowledge graphs (e.g., inferring missing relationships). - Molecular property prediction. - Traffic prediction in road networks. - Fraud detection in financial networks.
Graph Neural Network (GNN) Code Example
Here's how we can define the layers of a simple Graph Neural Network (GNN):
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
import tensorflow.keras.backend as K
class GraphConvolutionLayer(layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, units, activation=None, **kwargs):
super(GraphConvolutionLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.units = units
self.activation = activation
def build(self, input_shape):
self.kernel = self.add_weight(
shape=(input_shape[1][-1], self.units),
initializer="glorot_uniform",
trainable=True
)
def call(self, inputs):
adjacency_matrix, node_features = inputs
# Graph convolution: A * X * W
support = K.dot(node_features, self.kernel)
output = K.dot(adjacency_matrix, support)
if self.activation:
output = self.activation(output)
return output
# Define the GNN model
def build_gnn(num_nodes, num_node_features, num_classes):
adjacency_matrix = layers.Input(shape=(num_nodes, num_nodes), name="adjacency_matrix")
node_features = layers.Input(shape=(num_nodes, num_node_features), name="node_features")
# Graph Convolution Layers
x = GraphConvolutionLayer(32, activation=tf.nn.relu)([adjacency_matrix, node_features])
x = GraphConvolutionLayer(16, activation=tf.nn.relu)([adjacency_matrix, x])
# Global Average Pooling and Classification Layer
x = layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D()(x)
output = layers.Dense(num_classes, activation="softmax")(x)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs=[adjacency_matrix, node_features], outputs=output)
# Instantiate the GNN model
gnn_model = build_gnn(num_nodes=10, num_node_features=5, num_classes=3)